What is Identification?
Identification asks the question: “Who are you?” When new users complete the onboarding process, they identify themselves. Some companies limit their identity management process to identification, taking users’ information at face value. This can be very risky.
Companies lack user verification, making it challenging to confirm real identities, leaving room for fraudsters to exploit fake names and stolen identities.
What is Identity Verification?
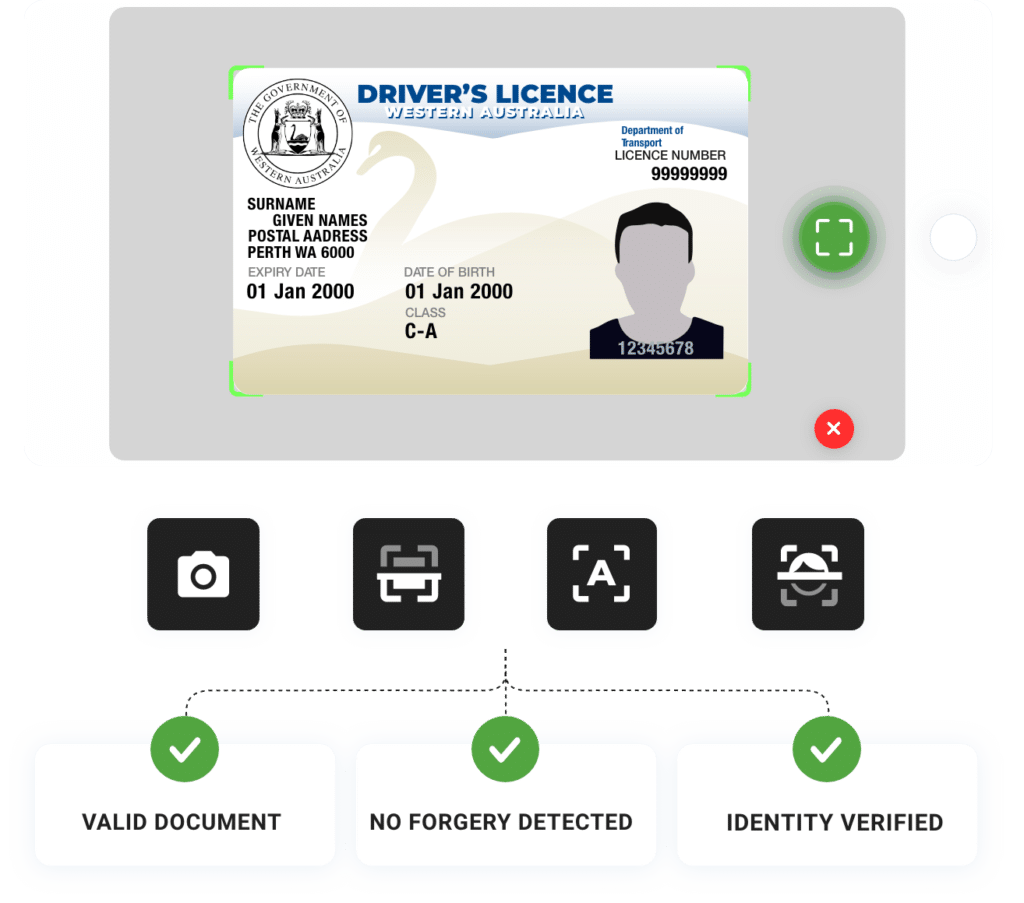
Verification moves from “Who are you?” to “Prove it.” Organisations must ask for verification to verify that a person is using their real name, address, phone number, and so on. Verification can be in the form of a driver’s license, ID card, or biometric data.
Verification of Identity is applied during the onboarding process. Identity verification can be integrated directly into a mobile app or provided as a web-based solution to help ensure customers are who they claim to be.
If a verification process isn’t in place, fraudsters with stolen identities or credentials can successfully use them. At the pandemic’s beginning, fraudsters stole identities to file dishonest unemployment claims and collect thousands of dollars in benefits. Once the breadth of fraud was identified, the AIC issued a report: Fraud and its relationship to pandemics and economic crises: From Spanish flu to COVID-19, advising and recognising the importance of identity verification services.
What is Authentication?
Authentication typically occurs every time a user signs on and can also be implemented when a user attempts a transaction or tries to access sensitive data.
Types of authentication fall into three main categories, also known as authentication factors:
- Knowledge – Something you know — information or secrets unique to you, including passwords, PINs and answers to security questions.
- Possession – Something you have. Possessions include smartphones, cards, key fobs and physical tokens that can either generate or receive one-time passwords or codes.
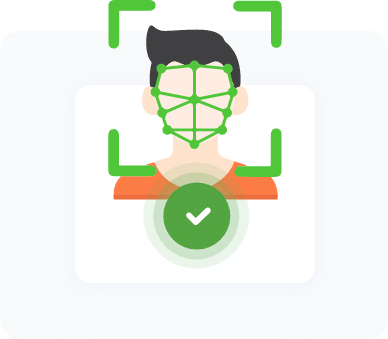
- Biometrics – Something you are: These are unique physical traits confirmed through fingerprint scans, voice recognition, and facial recognition.
What’s the Difference between Identification, Identity Verification and Authentication?
Identification is the first step in the process, where users provide information about themselves whilst progressing through the onboarding process. While a legitimate user will provide accurate information, a fraudster can give false or stolen information.
Verification forces the user to prove the information they provided is accurate. Because stolen identities can be used to set up accounts, this step stops fraudsters unable to provide the required proof of identity from creating fake accounts. Users may be asked to give a facial scan, a driver’s license copy, or another form of verification.
Authentication also requires users to prove their identities. Methods used for verification are also used for authentication, including fingerprint scans and facial recognition.
To learn more about the importance of ensuring users are who they claim to be, read our blog “why businesses are using instant identity verification” or contact Scantek today.